The Date/Time functions evaluate the date and time values in the YYYY/MM/DD format. You can customize the date/time format as per the provided Date/Time patterns in this page.
This function returns the UNIX time when the search starts. Unlike other functions, this function does not take any argument.
Syntax:
| process eval("identifier=now()")
Example:
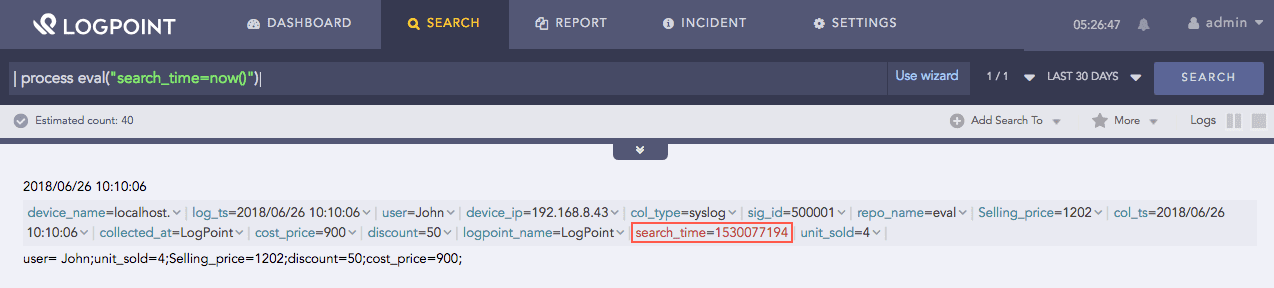
| process eval("search_time=now()")
The above example returns the UNIX time of the search process in the search identifier.
Now function¶
This function accepts two arguments, a UNIX time X, and a relative time specifier Y as inputs, and returns a UNIX time by adding or deducting the value of Y from the value of X.
Syntax:
| process eval("identifier=relative_time(X, Y)")
The operator used in Y can be either + or -.
The format specifier of time is s for a second, m for a minute, h for an hour, d for a day and w for a week.
Example:
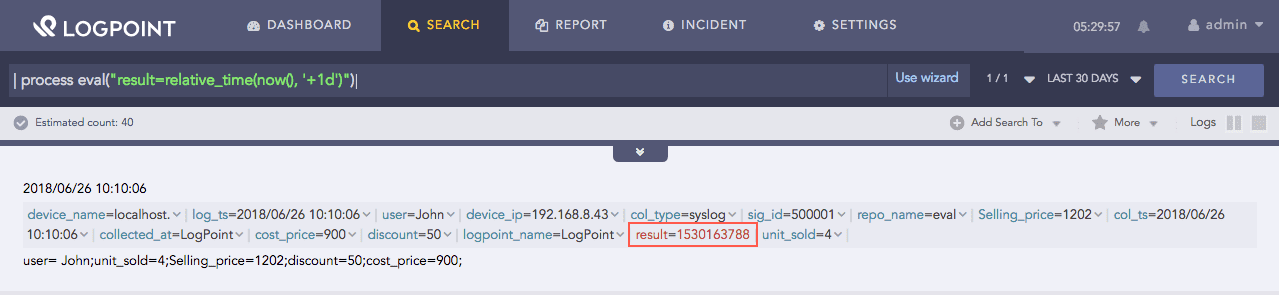
| process eval("result=relative_time(now(), '+1d')")
The above example adds time equivalent of 1 day to the current UNIX time and returns it in the result identifier.
Relative time function¶
This function accepts a UNIX time X and returns the time as a string using the date and time format specified in Y. The UNIX time value must be in seconds.
Syntax:
| process eval("identifier=strftime(X, Y)")
Example:
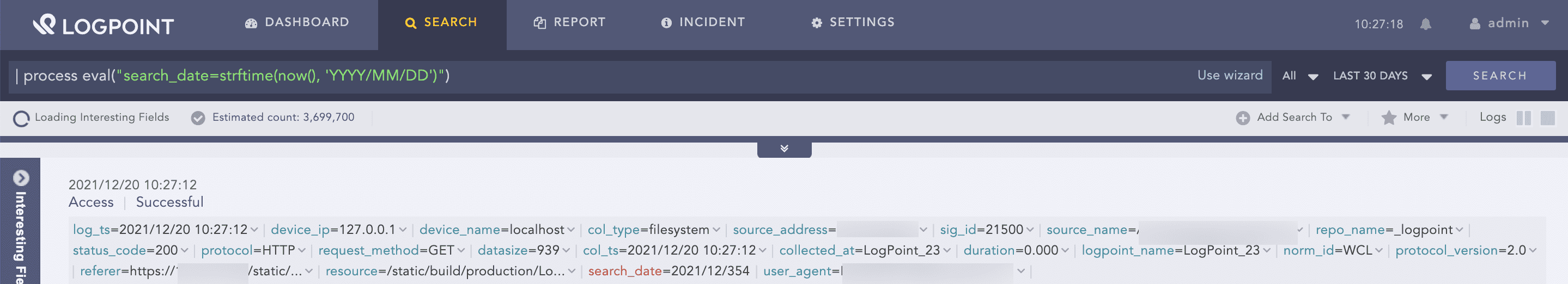
| process eval("search_date=strftime(now(), 'YYYY/MM/DD')")
The above example accepts the current UNIX time and returns the time in YYYY/MM/DD format in the search_date identifier.
Strftime function for day in year¶
Example:
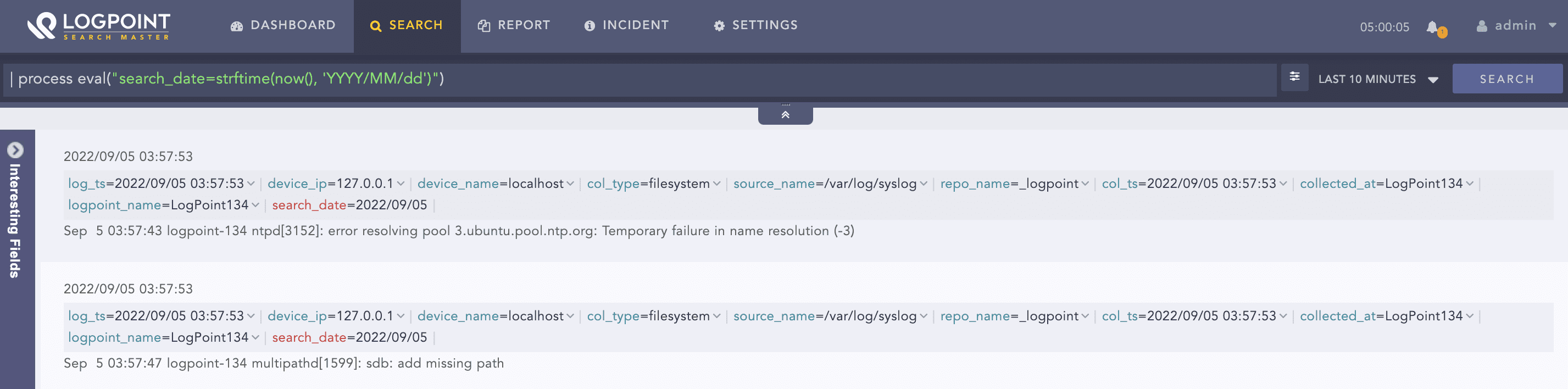
| process eval("search_date=strftime(now(), 'YYYY/MM/dd')")
The above example accepts the current UNIX time and returns the time in YYYY/MM/dd format in the search_date identifier.
Strftime function for day in month¶
The Timezone parameter in the strptime function converts date and time values based on timezone, defined by a fixed offset from Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). By default, the timezone of a machine is used for the conversion. It is an optional parameter.
Syntax:
GMTOffsetTimeZone:
GMT Sign Hours : Minutes
Sign: one of
+ -
Hours:
Digit
Digit Digit
Minutes:
Digit Digit
Digit: one of
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Example:
| process eval("identifier=strftime(now(), 'yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss', 'GMT+4:45')")
This function accepts a human readable time specified in X and converts it into a UNIX timestamp using the date and time format specified in Y.
Syntax:
| process eval("identifier=strptime(X, Y)")
Example:
| process eval("searchtime=strptime('2017-12-12', 'yyyy-mm-dd')")
The above example accepts the human readable time and converts it to a UNIX timestamp. It returns the converted time in the searchtime identifier.
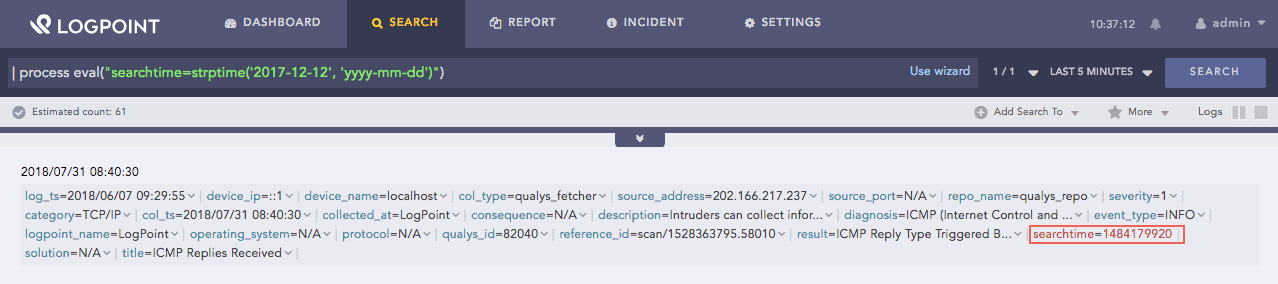
Strptime function¶
The Timezone parameter in the strptime function converts date and time values based on timezone, defined by a fixed offset from Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). By default, the timezone of a machine is used for the conversion. It is an optional parameter.
Syntax:
GMTOffsetTimeZone:
GMT Sign Hours : Minutes
Sign: one of
+ -
Hours:
Digit
Digit Digit
Minutes:
Digit Digit
Digit: one of
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Example:
| process eval("identifier=strptime('2022-08-12', 'yyyy-MM-dd', 'GMT-9:45')")
This function takes no argument and returns the UNIX time on which the eval process command processes the command. The returned time is the time when the eval command processed the event.
Syntax:
| process eval("identifier=time()")
Example:
| process eval("process_time=time()")
The above example returns the time of the eval command execution in the process_time identifier.
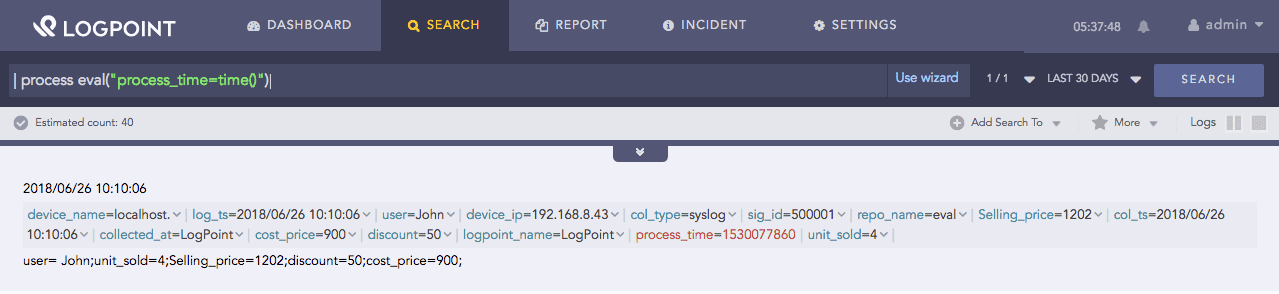
Time function¶
The list of all possible patterns in the date/time function.
Letter |
Date or Time Component |
Presentation |
Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
G |
Era designator |
Text |
AD |
y |
Year |
Year |
1996; 96 |
Y |
Week year |
Year |
2009; 09 |
M |
Month in year (context sensitive) |
Month |
July; Jul; 07 |
L |
Month in year (standalone form) |
Month |
July; Jul; 07 |
w |
Week in year |
Number |
27 |
W |
Week in month |
Number |
2 |
D |
Day in year |
Number |
189 |
d |
Day in month |
Number |
10 |
F |
Day of week in month |
Number |
2 |
E |
Day name in week |
Text |
Tuesday; Tue |
u |
Day number of week (1 = Monday, …, 7 = Sunday) |
Number |
1 |
a |
Am/pm marker |
Text |
PM |
H |
Hour in day (0-23) |
Number |
0 |
k |
Hour in day (1-24) |
Number |
24 |
K |
Hour in am/pm (0-11) |
Number |
0 |
h |
Hour in am/pm (1-12) |
Number |
12 |
m |
Minute in hour |
Number |
30 |
s |
Second in minute |
Number |
55 |
S |
Millisecond |
Number |
978 |
z |
Time zone |
General time zone |
Pacific Standard Time; PST; GMT-08:00 |
Z |
Time zone |
RFC 822 time zone |
-0800 |
X |
Time zone |
ISO 8601 time zone |
-08; -0800; -08:00 |
We are glad this guide helped.
Please don't include any personal information in your comment
Contact Support